Previously, we have written articles on various Linux commands like ls, ps, scp, history, and many more present on our website. Today, we will take a look at the WC command.
WC stands for “Word Count.” And as the name implies, the wc command is used for counting purposes. It prints out the number of lines, word count, byte, and characters count present in the file passed to the command. When you run this command on a file without any additional parameters/ arguments, we will print the result in four columns:
- First column: It shows the number of lines in the file.
- Second column: This shows the number of words in the file.
- Third column: This shows the number of characters present in the file.
- Fourth column: It shows the name of the file you passed as an argument.
WC command
Syntax:
wc [options] [file_name]
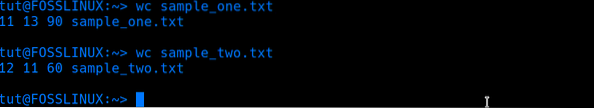
Consider the two files below, sample_one and sample_two. Sample_one contains a list of Linux distributions, while Sample_two includes a list of programming languages.

By parsing only the filename in the wc command, we get the results below:
wc sample_one.txt wc sample_two.txt
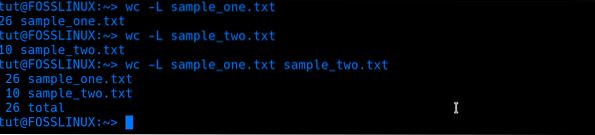
A fantastic feature with the WC command is that you can also pass multiple files. Check out the command below:
wc sample_one.txt sample_two.txt

From the output shown image above, the first line shows the results for sample_one.txt, and the second line shows results for sample_two.txt. However, you will notice there is a third line which we will call Total. This one shows the sum of the results from the two files. It displays the total number of lines, words, and characters of all the files passed.
WC command options
WC is a simple command to work with and comes with only a handful of options to select from:
-l, --lines - Prints the number of lines present in the file\-w, --words - Print the total number of words in the file (word count).-m, --chars -Prints the number of characters in the file.-L, --max-line-Length - Prints the longest line in the file.-c, --bytes - Prints the total number of bytes in the file.
Let's now look at every option and how we can use it on various files.
1. -l, -lines Option
This option prints the total number of lines in the file. The information is printed in two columns. The first column shows the number of lines present, and the second column showing the name of the file passed.
wc -l sample_one.txt

2. -w, -words Option
The -w or --words option shows the total number of words present in a file. It prints the results in two columns. The first column shows the total number of words, and the second column showing the name of the file.
wc -w sample_one.txt

3. -m, -chars option
The -m or --chars option shows the total number of characters in the file. It prints the results in two columns. The first column shows the total number of characters in the file, and the second column shows the name of the file.
wc -m sample_one.txt

4. -L, -max-line-Length Option
The -L (uppercase) option prints the length (number of characters) of the longest line in the file. In the file sample_one.txt, the longest line is “Elementary OperatingSystem,” and in sample_two.txt, the longest line is “Javascript.” When you pass more than one filename, unlike the other options, which would show the total, this option indicates the number of characters of the two files' longest line.
wc -L sample_one.txt wc -L sample_one.txt sample_two.txt
5. -c, -bytes Option
This option shows the count of bytes present in the file. It prints the results in two columns. The first column shows the total number of bytes in the file, and the second column showing the name of the file passed.
wc -c sample_one.txt

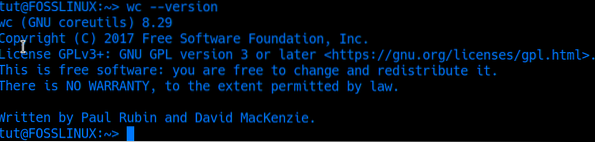
6. -version Option
This option doesn't take any filename but only shows the version of wc currently running on your system.
wc --version
Application of WC Command
1. Count the Number of Files and Folders Present in a Directory
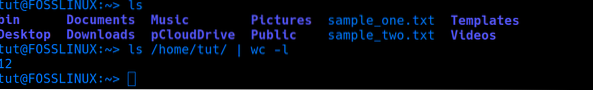
The ls command is used to list all the contents in a directory. When piped with the wc -l command, we could count the number of files and folders present in the directory. See the command below:
ls /home/tut | wc -l
2. Count the Number of Users
To list the users in a system, we could use the commands cat /etc/passwd or getent passwd. If we just wanted a count of the total number of users, we could pipe the output of, say getent passwd to wc -l as shown below:
getent passwd | wc -l

Conclusion
I believe this post has given you a clear guide on using the WC (word count) command and the various options available. You can perform much more powerful tasks by combining the wc command with other Linux commands. If you come across any challenges, you can use the command wc --help. Please feel free to leave any queries or comments regarding this post.
 Phenquestions
Phenquestions